Healthcare Solutions
Entropic provide unique solutions for the various ventilation needs of the modern healthcare sector
The main features of this unit are:
- Ultra clean air flow (1000 times greater than FFP1 masks*)
- Large air flow (up to 700 l/s)
- Significantly reduces the pathogen concentration in room air
*The unit removes 99,995% (MPPS 100-200nm) of the particles from the recirculated airflow, which means that the filtration efficiency is 1000 times higher than in Respirator masks (USA:N95/Europe:FFP1) recommended by CDC for HCP caring for patients with confirmed or suspected respiratory pathogens including SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19.
Ventilation is used extensively in all types of healthcare premises to provide a safe and comfortable environment for patients and working staff. More specialized ventilation is provided in areas with more specific requirements, such as patient treatment areas which include operating departments, critical care areas and isolation units.
It is also installed to ensure observance with quality certainty of processed items in pharmacy and sterile services departments, and to protect staff from harmful organisms and toxic substances (for example in laboratories).
The sophistication of ventilation in healthcare premises is increasing. Patients and staff have a right to expect that it will be designed, installed, operated and maintained to standards that will enable it to fulfill its desired functions reliably and safely.
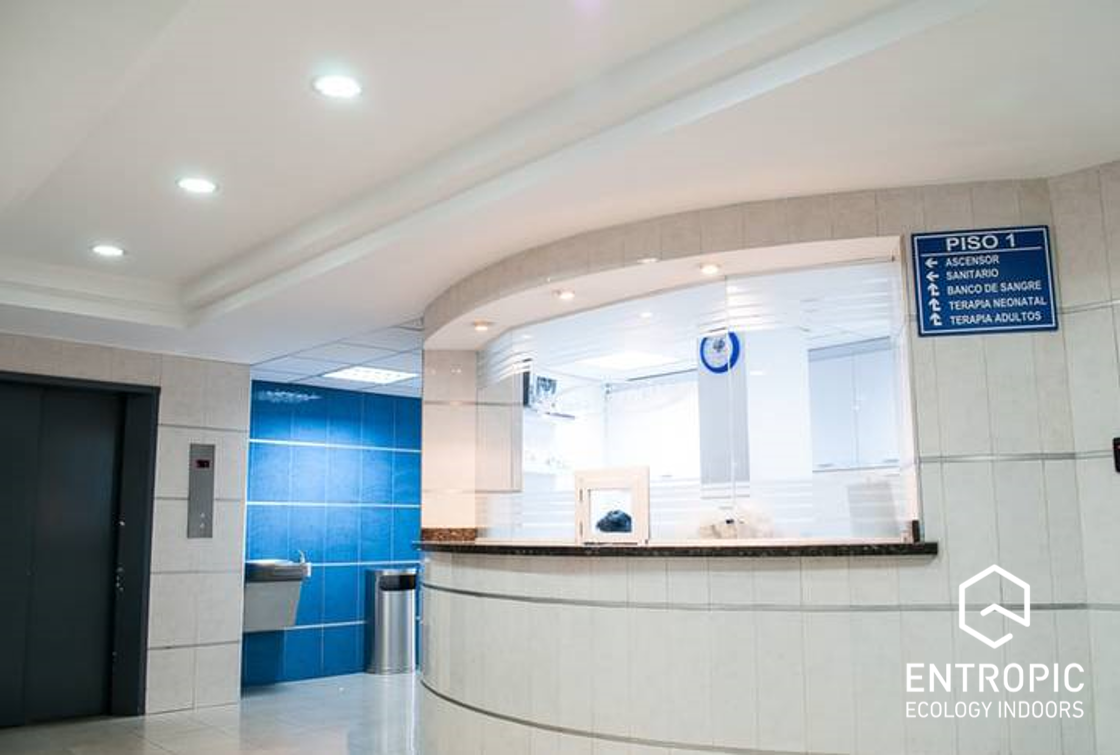

Zoning of the building
The efficiency and effectiveness of any ventilation or air-conditioning installation depends largely on the zoning and control of the installation. The factors to consider when determining the zoning of a ventilation system for a building or department are:
- Periods of occupancy
- Fresh-air/ventilation requirements
- Smoke control
Where the ventilation system is not only tempering the air, but also providing the heating and/or cooling requirements, the following additional factors will need to be considered:
- Internal or peripheral location
- Orientation of windows
- Variation in internal loads
- Level of control required
Entropic’s patient room solutions are designed using chilled beams. This is an extremely energy efficient system that reaches the desired air temperature and velocity and has a low operating sound level. Chilled beams are suitable for healthcare projects as they are easy to maintain and clean, keeping the environment as hygienic as possible. An example of a chilled beam system is St. Anne’s Day Care Ward in St. Vincent’s Hospital. Our solution was to replace the existing radiant panels with active chilled beams to provide heating, cooling and ventilation.
Selection of design criteria
Minimum fresh-air requirements
The dilution of body odours is the critical factor while determining ventilation requirements. Where natural ventilation or full fresh-air systems are used, all ventilation air will be fresh.
Where odour dilution is the overriding factor, it is recommended that 10 liters/ second/ person should be taken as the minimum ventilation rate.
In non-standard applications such as laboratories, aseptic suites, operating departments etc, the particular requirements for each area should be considered independently in order to determine the overriding minimum requirement for ventilation.
Limiting supply air conditions
For most applications in healthcare buildings the critical factor is the temperature differential between the supply and room air rather than the actual temperature of the supply air. The maximum recommended supply-to-room-air temperature differential is:
- Summer cooling: –7 K
- Winter heating: +10 K.
In areas that have high heat gains from equipment (for example critical care areas), the summer cooling temperature differential limit given above may result in excessive air-change rates.
A differential of up to –10 K is acceptable in these circumstances, providing the supply-air diffusers are of a type that provide good mixing.
If a humidifier is fitted, it is necessary to keep supply-air humidity below 70% during winter in order to minimize the risk of condensation on cold surfaces.
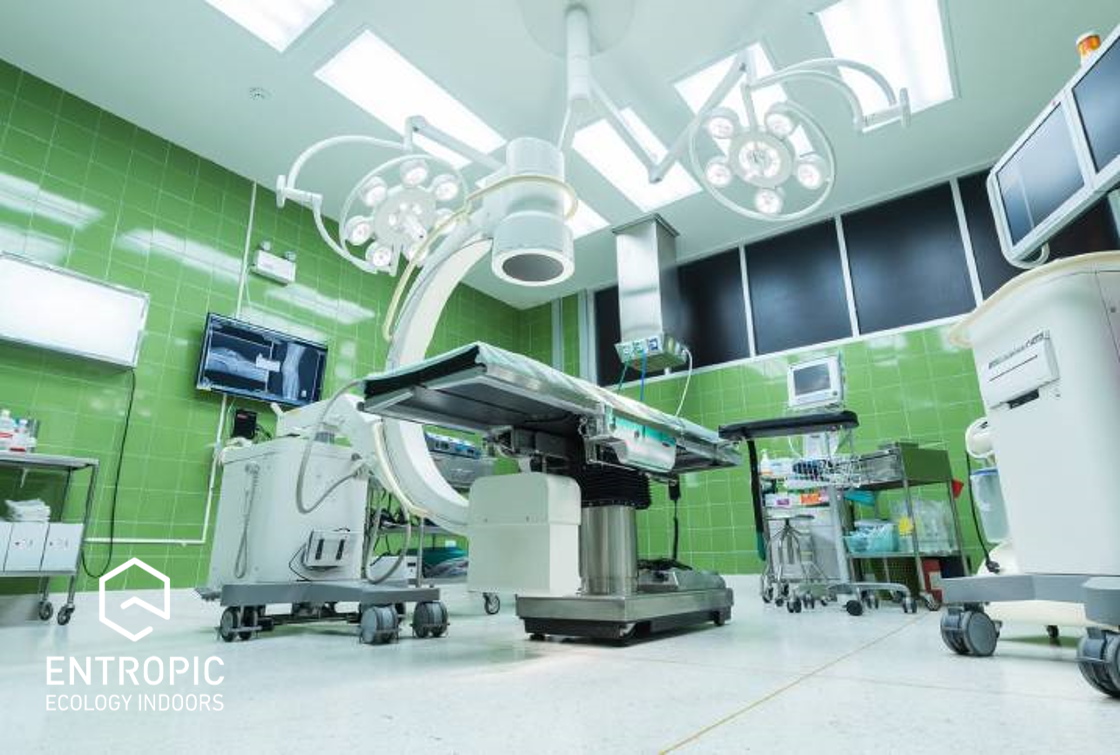
Air purity
In healthcare premises, the standard of filtration will depend on the activities within the occupied spaces. With the exception of specialist areas (for example manufacturing pharmacies), aerobiological requirements are not stringent, and filtration is only required to:
- Maintain hygienic conditions for the health and welfare of occupants, or for processes such as food preparation
- Protect finishes, fabrics and furnishings in order to reduce redecoration costs
- Protect equipment either within the supply air system (that is, to prevent blocking of coils), or in the space itself to prevent dust build-up
Given that almost all viable particles originate from the occupants of a space and not from the incoming air, dilution is the more important factor aerobiologically. Therefore, for general areas a G4 filter is suitable. More critical areas will require an F7 filter. High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters are required only in ultra-clean systems.
Noise levels
Noise is typically generated by fans, ductwork fittings, dampers and grilles. The specified maximum noise level will depend on the activities within the occupied spaces.
The reduction of tonal components needs to be given attention. High tonal components from air diffusers can weaken concentration over longer periods even when the overall noise level is low.
Attenuation should be incorporated into the ductwork system or plant arrangement as necessary to reduce noise from fans and plant items in order to achieve acceptable limits within rooms at the design air flows.
The designer must also consider noise escaping to the external environment, and this must not be unacceptable to occupants of adjacent areas or buildings.
The overall noise levels should not exceed the values given in Health Technical Memorandum
08-01 –‘Acoustics’.
Plant noise is subject to the Control of Noise at Work Regulations 2005 and should not exceed 80 dB(A) within a plant room. It should be reduced to lower levels where the plant is near to departments sensitive to noise.
It is necessary to consider each of these parameters in both summer and winter conditions to ensure satisfactory operation of the air-terminal device, as warm jets behave very differently from cold jets.
A warm jet tends to rise until it attaches itself to a horizontal surface, while a cold jet falls. It must be taken care of so it does not lead to unacceptable temperature gradients in winter, or excessive air velocities in the occupied zone in summer.
In order to ensure satisfactory air movement within a space, it is necessary to consider interaction between air movement from adjacent terminals and ceiling-mounted fixtures (light fittings etc), as well as interaction between air movement and room surfaces.
Air Handling Units Projects
Download our selection software in Resources to get detailed information about products suitable for healthcare projects.
Check our Healthcare site references and case studies by clicking on the button below.






